Stone tools suggest Homo sapiens settled in Europe in three waves – study
When modern humans spread across and settled Europe during the Paleolithic age, they did so in three distinct settlement waves.
This is the conclusion from a peer-reviewed study published on May 3 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Ludovic Slimak of the Centre national de la recherche scientifique (CNRS) and University of Toulouse III, France.
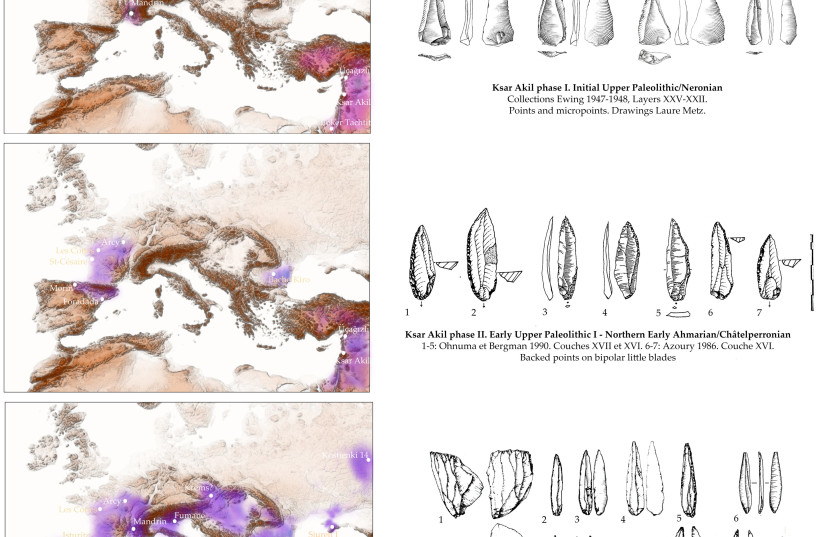
In this study, Slimak carried out comparative analyses of stone tool technology from sites across western Eurasia, with a special focus on two sites: Ksar Akil in Lebanon and Grotte Mandrin in France.
Central issues
The issues he aimed to shed more light on answer were – how did humans arrive and settle in Europe, and how did they interact with the Neanderthals, who were already there?
During the research, Slimak identified a similar sequence of three technological phases in the two sites he focused the study on, suggesting three distinct waves of migration of Homo sapiens across Europe.
 The paper provides evidence for three distinct waves of early migration of Sapiens in Europe from the East Mediterranean coast. (credit: Ludovic Slimak, CC-BY 4.0)
The paper provides evidence for three distinct waves of early migration of Sapiens in Europe from the East Mediterranean coast. (credit: Ludovic Slimak, CC-BY 4.0)The three key phases of the earliest Levantine Upper Palaeolithic have very precise technical and chronological counterparts in Western Europe, recognized from the Rhône Valley to Franco-Cantabria, Slimak found. These technical connections, according to him, suggest three distinct waves of expansion into Europe between 55–42 thousand years ago.
“Until 2022, it was believed that Homo sapiens had reached Europe between the 42nd and 45th millennium. The study shows that this first sapiens migration would actually be the last of three major migratory waves to the continent, profoundly rewriting what was thought to be known about the origin of sapiens in Europe,” Slimak explained.
“Chatelperronian culture, one of the first modern traditions in western Europe and since then attributed to Neanderthals, should in fact signal the second wave of Homo sapiens migration in Europe, impacting deeply our understanding of the cultural organization of the last Neanderthals.”
Slimak identified three technical traditions, each one linking sites in the Middle East and Europe, and pointing to one of the Homo sapiens’ migration waves.
Phase 1, around the 54th millennium, is represented by the Neronian/Initial Upper Palaeolithic; phase 2 by the Chatelperronian/Early Upper Palaeolithic around the 45th millennium, and phase 3 by the Protoaurignacian/Southern Early Ahmarian Palaeolithic around the 42nd millennium.





Comments are closed.